
Liabilities can be described as an obligation between one party and another that has not yet been completed or paid for. They are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits, including money, goods, or services. Liabilities in financial accounting need not be legally enforceable; but can be based on equitable obligations or constructive obligations. An equitable obligation is a duty based on ethical or moral considerations. A constructive obligation is an obligation that is implied by a set of circumstances in a particular situation, as opposed to a contractually based obligation. Recognizing liabilities in the balance sheet can be tricky and a confusing bookkeeping responsibility.
- As a small business owner, you’re going to incur different types of liabilities as you operate.
- Examples of contingent liabilities are the outcome of a lawsuit, a government investigation, or the threat of expropriation.
- Our popular accounting course is designed for those with no accounting background or those seeking a refresher.
- Small businesses that aren’t required to comply with the US GAAP may opt not to consider contingencies in financial reporting.
- In short, liabilities are the opposite of total assets a company owns.
- Companies segregate their liabilities by their time horizon for when they’re due.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Fortunately, you can answer this question by calculating your break-even point. Try FreshBooks for free by signing up today and getting started on your path to financial health.
- A liability account in accounting represents the various financial obligations a company owes to others, recorded on its balance sheet.
- The outstanding money that the restaurant owes to its wine supplier is considered a liability.
- The current/short-term liabilities are separated from long-term/non-current liabilities.
- A constructive obligation is an obligation that is implied by a set of circumstances in a particular situation, as opposed to a contractually based obligation.
Rules for Income or Revenue Accounts
- If both sides of this basic accounting equation are the same, then your book’s “balance” is correct.
- Financial liabilities can be either long-term or short-term depending on whether you’ll be paying them off within a year.
- Also sometimes called “non-current liabilities,” these are any obligations, payables, loans and any other liabilities that are due more than 12 months from now.
- When you borrow funds, you’ll have to pay interest to the creditor.
- Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers.
- These liabilities may or may not materialize, and their outcome is often uncertain.
Short-term liabilities, also known as current liabilities, are obligations that are typically due within a year. On the other hand, long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, extend beyond a year. Besides these two primary categories, contingent liabilities and other specific cases may also exist, further adding complexity to accounting practices. Liabilities in accounting are recorded as financial obligations, but these act as the most efficient resource for companies to fund capital expansion.

Balance Sheet Outline
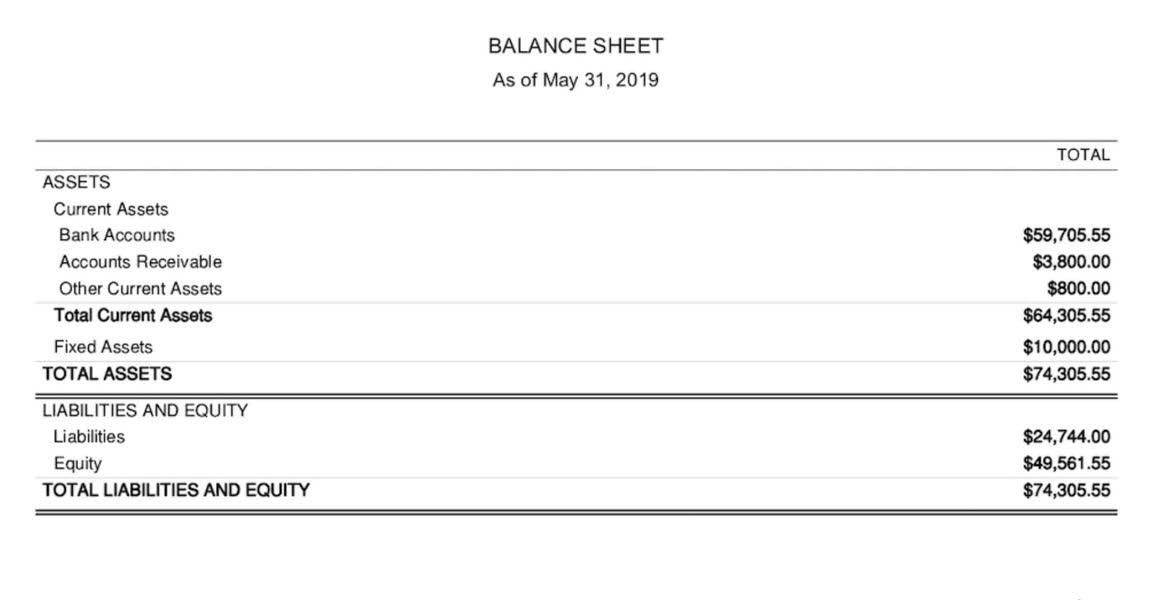
Accurately accounting for pension obligations can be complex and may require actuarial valuations to determine the present value of future obligations. The portion of the vehicle that you’ve already paid for is an asset. Financial liabilities can be either long-term or short-term depending on whether you’ll be paying them off within a year.

To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
- Liabilities are on the right side of the balance sheet, and these accounts have a normal credit balance.
- Liabilities in accounting are any debts your company owes to someone else, including small business loans, unpaid bills, and mortgage payments.
- There are also cases where there is a possibility that a business may have a liability.
- Keep up with Michelle’s CPA career — and ultramarathoning endeavors — on LinkedIn.
- When it comes to short-term liquidity measures, current liabilities get used as key components.
- Basically, these are any debts or obligations you have that need to get paid within a year.
Short-term, or current liabilities, are liabilities that are due within one year or less. They can include payroll expenses, rent, and accounts payable (AP), money owed by a company to its customers. Lease payments are a common type of other liability in accounting. These are the periodic payments made by a lessee (the business) to a lessor (property owner) for the right to use an liabilities accounts asset, such as property, plant or equipment. In accounting terms, leases can be classified as either operating leases or finance leases. An operating lease is recorded as a rental expense, while a finance lease is treated as a long-term liability and an asset on the balance sheet.

Expenses can be paid immediately with cash or the payment could be delayed which would create a liability. Just as your debt ratios are important to lenders and investors looking at your company, your assets and liabilities will also be closely examined if you are intending to sell your company. Potential buyers will probably want to see a lower debt to capital ratio—something to keep in mind if you’re planning on selling your business in the future. Any debt a business or organization has qualifies as a liability—these debts are legal obligations the company must pay to third-party creditors. Examples of liabilities include deferred taxes, credit card debt, and accounts payable. Liability accounts are crucial in understanding a company’s financial health, mapping out obligations like accounts payable, long-term debts, and accrued expenses.

Accounts payable represents the amounts owed to vendors or suppliers for goods or services the company had received on credit. The amount is supported by the vendors’ invoices which had been received, approved for payment, and recorded in the company’s general ledger account Accounts Payable. However, the total liabilities of a business have a direct relationship with the creditworthiness of an entity. A larger amount of total liabilities is not in-and-of-itself a financial indicator of poor economic quality of an entity.
But not all liabilities are expenses—liabilities like bank loans and mortgages can finance asset purchases, which are not business expenses. A company may take on more debt to finance expenditures such as new equipment, facility expansions, or acquisitions. When a business borrows money, the obligations to repay the https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ principal amount, as well as any interest accrued, are recorded on the balance sheet as liabilities.
Definition of Liability
It can appear like spending and liabilities are the same thing, but they’re not. Expenses are what your organization regularly pays to fund operations. The commitments and debts owed to other people are known as liabilities. But there are other calculations that involve liabilities that you might perform—to analyze them and make sure your https://www.bookstime.com/ cash isn’t constantly tied up in paying off your debts.





Leave a Reply